Published by:
Renji Elsa Jacob, M-Tech in Electronics & Electrical Engineering
Overview of electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is a structure to direct and control electric currents to perform some useful functions like data transfer, signal amplification, and computation.
Electric current is the flow of electric charge while the electric circuit is the conductive path for the flow of current. A conductive wire is used to provide a connection between the voltage source and the load.
When can we call a circuit as an electronic circuit?
A circuit consisting of specific electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors, and diodes connected by conductive wires through which electric current can flow is called an electronic circuit.
The circuits should provide a path for the current to flow. We can say that a circuit must form a loop or to be a circuit, this path must start and end at the same point. Both the electronic circuit and the electrical circuit have the same definition, but electronic circuits tend to be low voltage circuits.
A Circuit can be called an electronic circuit only if it has at least one active component.
An electronic circuit contains many types of components, which are divided into two types:
- Active components like transistors, diodes, IC’s; and
- Passive components like capacitors, resistors, inductors, etc.
The following things are taken into consideration while designing an electronic circuit:
- Basic electronic components: capacitors, resistors, diodes, transistors, etc.
- Power sources: Signal generators and DC power supplies.
- Measurement and analysis instruments: Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO), multimeters, etc.
Elements of the Electronic Circuit
Circuits can be simple or complex. The simplest circuits have three basic elements:
- Voltage Source: This is a two-terminal device like a battery or power systems etc. that provides a voltage in the circuit that causes the current to flow.
- Load: It represents the actual work done by the circuit. The load consumes power. The load can be a simple bulb or a combination of components like resistors, capacitors, transistors, etc.
- Conductive Path: It provides a way through which the current flows. The path starts from the voltage source, travels through the load, and then returns to the voltage source.
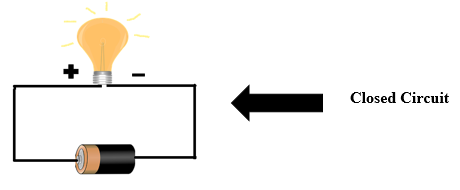
1. Closed Circuit: The circuit is said to be a closed circuit when a circuit is complete and forms a loop that allows current to flow.
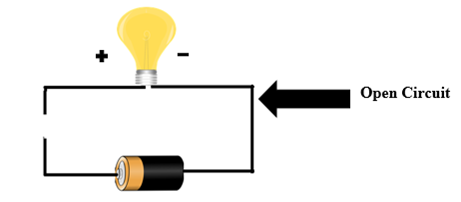
2. Open Circuit: The circuit is called an open circuit, if any part of the circuit is disconnected or disrupted so that a loop is not formed, current cannot flow.
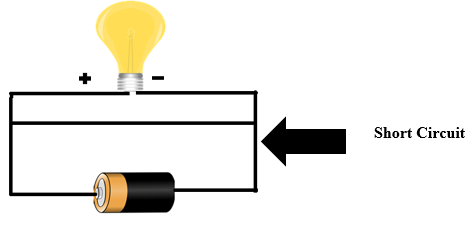
3. Short Circuit: If a circuit does not have a load that is called a short circuit. For example, if the bulb is connected to the circuit and a direct connection is existing between the battery’s negative terminal and its positive terminal, too. If there is a direct connection between the battery’s negative and positive terminal, the current will flow through it rather than passing through the circuit. In a short circuit, current flows at dangerously high levels. Electronic components get damaged if short circuits happen, cause a battery to explode, or maybe start a fire.
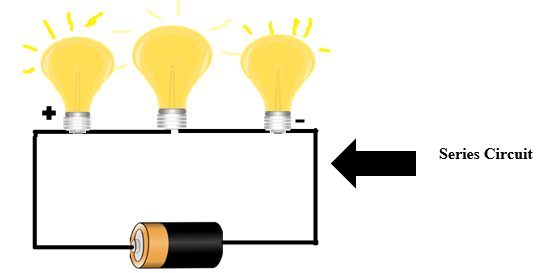
4. Series Circuit: When 2 or more loads are connected in series with each other, then it is called a series circuit.If anyone load gets fuse, then the other load does not get power supply.
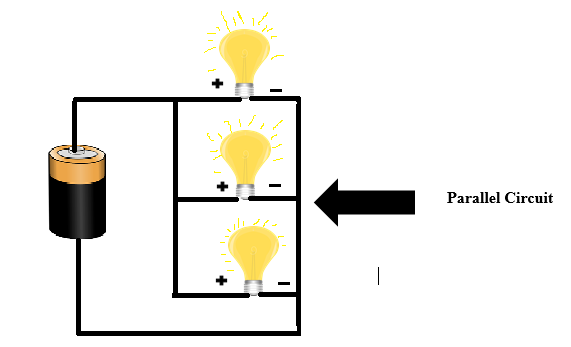
5. Parallel Circuit: When 2 or more loads are connected in parallel to each other, then it is called Parallel Circuit. Here, the voltage capacity of all loads must be equal to the input supply. The power of “load” can be different. In a parallel circuit, if one load gets a fuse, then the rest of the load will still get power supply.
Types of Electronic Circuit
A circuit can be classified into different types:
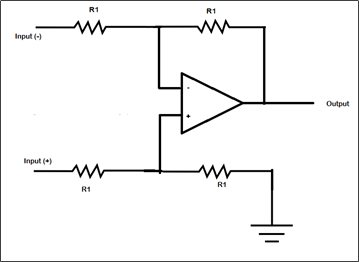
- Analog Electronic circuit: The circuit in which the signals may vary continuously with time to equivalent to information being represented.
Example: Voltage amplifiers, Power amplifiers, etc.
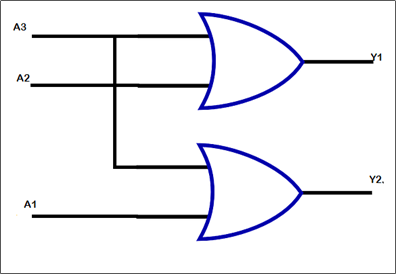
- Digital Electronic circuit: A circuit where the signal is either of the two discrete levels – ON / OFF or True / False or 0 / 1. Transistors are used to create logic gates to perform Boolean logic.
Example: Multiplexers, De-multiplexers, Encoders, Decoders, etc.
3. Mixed-signal circuit: It contains elements and properties of both Analog Circuit and Digital Circuit. Hence it is also called hybrid circuits.
Example: Timers, ADCs (Analog to digital converters), DACs (Digital to Analog converters)

No Comments